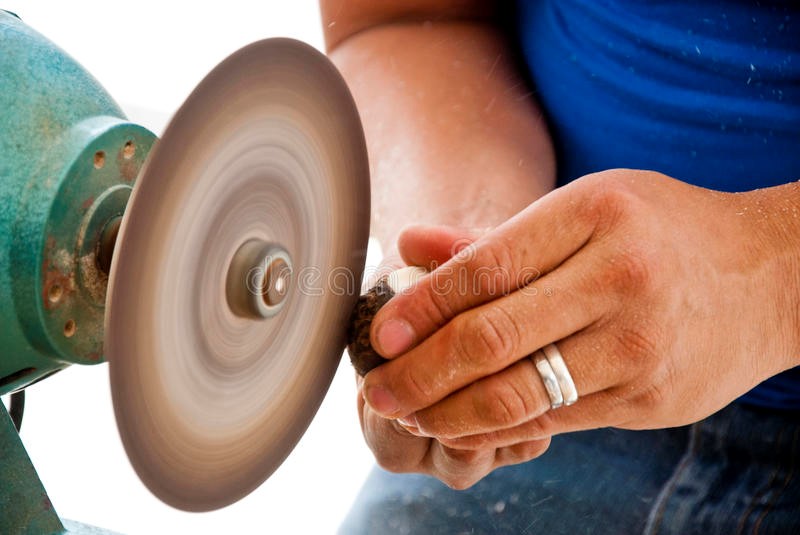
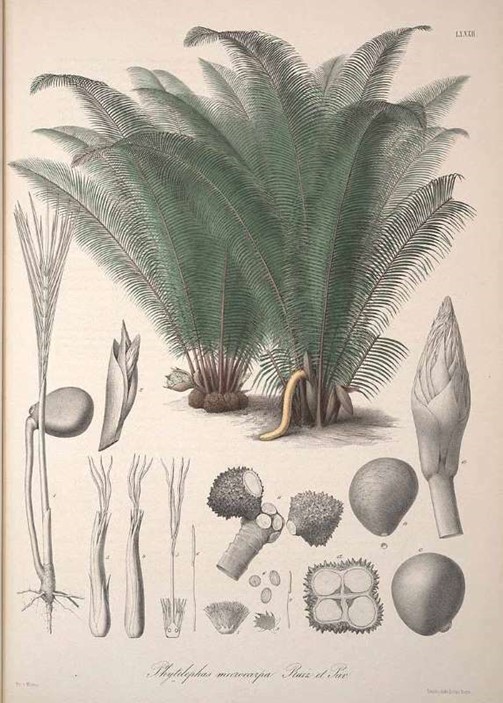
Tagua Ivory
The allure of ivory from elephants, walruses or sperm whales has resulted in the decimation of those species. The quest for a replacement has simply increased the volume of plastics being produced throughout the world without obtaining the qualities of beauty and hardness that carvers demand.
The discovery of the palm tree, Phytelephas (literally meaning “elephant plant”) in the jungles of South America found a replacement source for animal ivory. Known locally as Tagua, it was found to produce a large nut that when dried becomes exceptionally hard, resilient, and tough. It is so hard, in fact, that when carved and polished to a high sheen, it has a beautiful cream color that glows with warmth and is only rivaled by animal ivory. Individual trees have been found to produce Tagua Ivory for over 100 years
The benefits of replacing animal ivory with vegetable ivory are 3-fold.
First- It saves endangered species. Pressure upon endangered species being killed for their ivory is significantly reduced.
Second- It saves the rainforest. the Tagua Ivory Palm, as a rainforest species in South America, can be worked as a renewable cash crop without chopping down the tree. Preservation of rainforests is much easier because rather than cutting the forests down to grow other cash crops, locals can make an income from Tagua harvesting and craft production. Normally, when rain forests are chopped down to make a farm or ranch, the thin tropical topsoil quickly erodes, and all nutrients are stripped out of the earth in just a few years leaving the ground unfit for farming. Communities are then forced to move further into the rainforest to start all over again.
Alternatively, keeping the rainforests strong and diverse produces great Tagua Ivory without having to add any chemical fertilizers or pesticides. This allows rainforest communities to be economically viable over the long-term growing organic and all natural products.
Lastly it helps local families. Tagua harvesting, and the artisanal production of crafts, produce incomes for entire families and communities. This helps them to become more self-reliant in regions that are economically challenged resulting in happier and healthier lives.